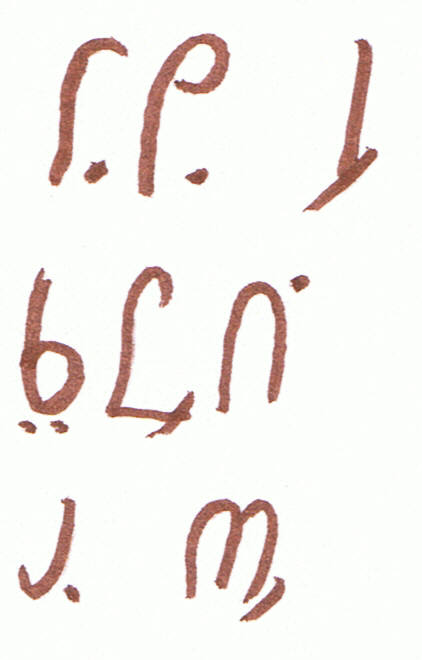Languages
Languages

Home | Author | Intro to the Period | Languages | Features
Conventions | Grammar | Verbal Forms | Modern-Old Tongue Dictionary | Old Tongue-Modern Dictionary | Old Hand
suffixes | combinations | examples
The use of this info is explained in Grammar.
| present | i |
| past | a |
| future | e |
| 1st person | ch |
| 2nd person | p |
| 3rd person | d |
| singular | — |
| plural | ma |
| continuing | ke |
| conditional | ara |
| pensive | obi |
| potential | ese |
| affirmative | — |
| negative | nyo |
I went to the trading post Tredin pos ni ichia
If you go to the trading post Tredin pos ni ipara
If we are not going to the trading post Tredin pos ni ichimaranyo
If you were going to the trading post Tredin pos ni ipaketara
He can go to the trading post Tredin pos ni idese
I might go to the trading post Tredin pos ni ichobi
We might be going to the trading post Tredin pos ni ichimaketobi
We would go to the trading post Tredin pos ni ichemobi
If you all might not be able to go to the trading post Tredin pos ni ipemaratobitesenyo OR ipemaratesetobyo OR ipemesetobitaranyo OR ipemobitesetaranyo
NB: In the last example, the first variation stresses the question of ability, "if you might not be ABLE," the second the uncertainty "if you MIGHT not be able," and the third and fourth, the condition "IF you might not be able." In addition, the third implies that the condition in question is the uncertainty, the fourth that it is the ability.